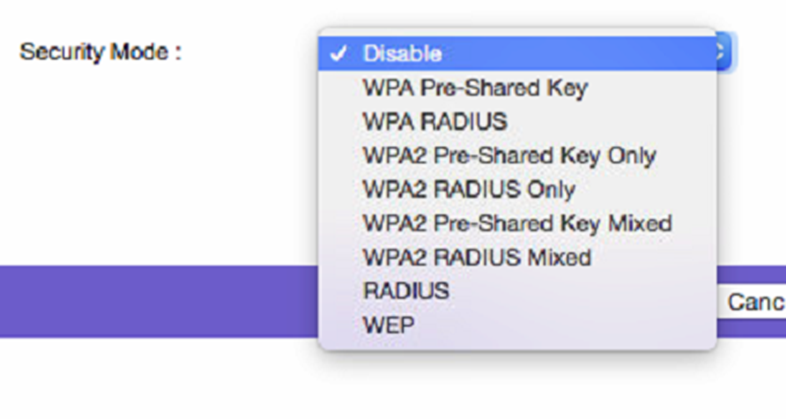
WPA, WPA2, WEP, RADIUS, Mixed, and Only
What to Choose?
Unless you need to support legacy computers, choose WPA2 Pre-Shared Key Only. Then choose AES as the WPA Algorithm.
Security Modes
WPA2 replaces WPA and supports AES . WPA2 has two ways of authenticating (Pre-Shared Key or RADIUS.) Pre-Shared Key Only is what most home networks will use. RADIUS requires a RADIUS server that most households lack, so you probably aren't going to use that. Further, if you need to support legacy computers, WPA2 also supports a Mixed mode that permits computers to connect via either WPA or WPA2 whereas the Only mode supports just WPA2.
- WPA2 Pre-Shared Key Only is best choice. It supports only the modern WPA2 access and uses a password (aka as a pre-shared key.)
- WPA2 Pre-Shared Key Mixed supports WPA2 and legacy WPA connections.
- WPA2 RADIUS Only requires a RADIUS server, which most home networks don't have.
- WPA2 RADIUS Mixed also supports use of WPA for legacy systems.
WPA replaces WEP and supports TKIP . Like the newer WPA2, the legacy WPA can have two ways of authenticating (Pre-Shared Key or RADIUS.) If you need to support WPA, just use WPA2 Mixed instead, because it supports both the legacy WPA and the newer WPA2.
- WPA Pre-Shared Key
- WPA RADIUS
RADIUS requires an external server for authentication. Most home networks do not have this.
WEP is obsolete.
WPA Algorithms
- AES is stronger than TKIP is. It's generally associated with WPA2.
- Temporal Key Integrity Protocol ( TKIP ) is weaker than AES is and is associated with WPA.
Sources
http://www.differencebetween.net/technology/difference-between-wpa-and-wpa2